The Ultimate Guide to Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Types, Costs, and Benefits
Implementing a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) involves upfront costs but offers significant long-term benefits. Read more to learn how.
Summary
Implementing a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) can transform lab operations—but it requires a smart cost-benefit analysis to justify the investment. From sample tracking to regulatory compliance, a LIMS offers automation that cuts manual errors and boosts productivity.
Key benefits of a well-implemented LIMS:
Saves time by automating data capture and reporting
Reduces human error and ensures data accuracy
Enhances compliance with industry regulations
Improves lab efficiency and decision-making
Delivers long-term ROI for labs of all sizes
Looking to build custom solutions for labs, healthcare, or any specialized domain? Explore our on-demand app development insights tailored for industry-specific software success.
Introduction
Many types of industries tend to have laboratories that generate a massive amount of data on a daily basis. This is true for labs in all industries, including healthcare, pharmaceutical, research, and more.
A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) provides a powerful solution by enabling laboratories to track and manage sample data, streamline workflows, and enhance regulatory compliance.
However, implementing a LIMS requires a significant investment, making it necessary to perform a cost-benefit analysis before taking the leap. A cost-benefit analysis is crucial to determine the potential return on investment (ROI). The cost of implementing a LIMS can vary and depends on the size of the laboratory, the number of users, and the level of customization required.
This blog explores the cost-benefit analysis of implementing a LIMS, highlighting the direct and indirect costs involved, as well as the tangible and intangible benefits it can bring to a laboratory environment.
What is a LIMS?

Before diving into the cost-benefit analysis, it is essential to understand what a LIMS is and what it does. A LIMS is a laboratory software solution designed to help laboratories manage and track data associated with samples, experiments, and processes. Its functionalities typically include:
Sample management and tracking
Data collection and storage
Workflow automation
Reporting and analytics
Regulatory compliance
Instrument integration
Quality assurance management
A LIMS can be used across various industries, including biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, research, environmental testing, and clinical labs, to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain high standards of accuracy and compliance.
In today’s fast-paced laboratory environment, effective management of data and resources is essential for success. Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) have emerged as vital tools for enhancing efficiency, ensuring compliance, and improving data accuracy.
It automates various processes, including sample tracking, data management, reporting, and compliance with regulatory standards. By streamlining laboratory operations, LIMS can significantly enhance productivity and data integrity.
Do you need a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS)?
Contact us today to learn how a tailored LIMS can transform your lab operations and streamline efficiency! Reach out to Acquaint Softtech for more information.
Types of LIMS Solutions
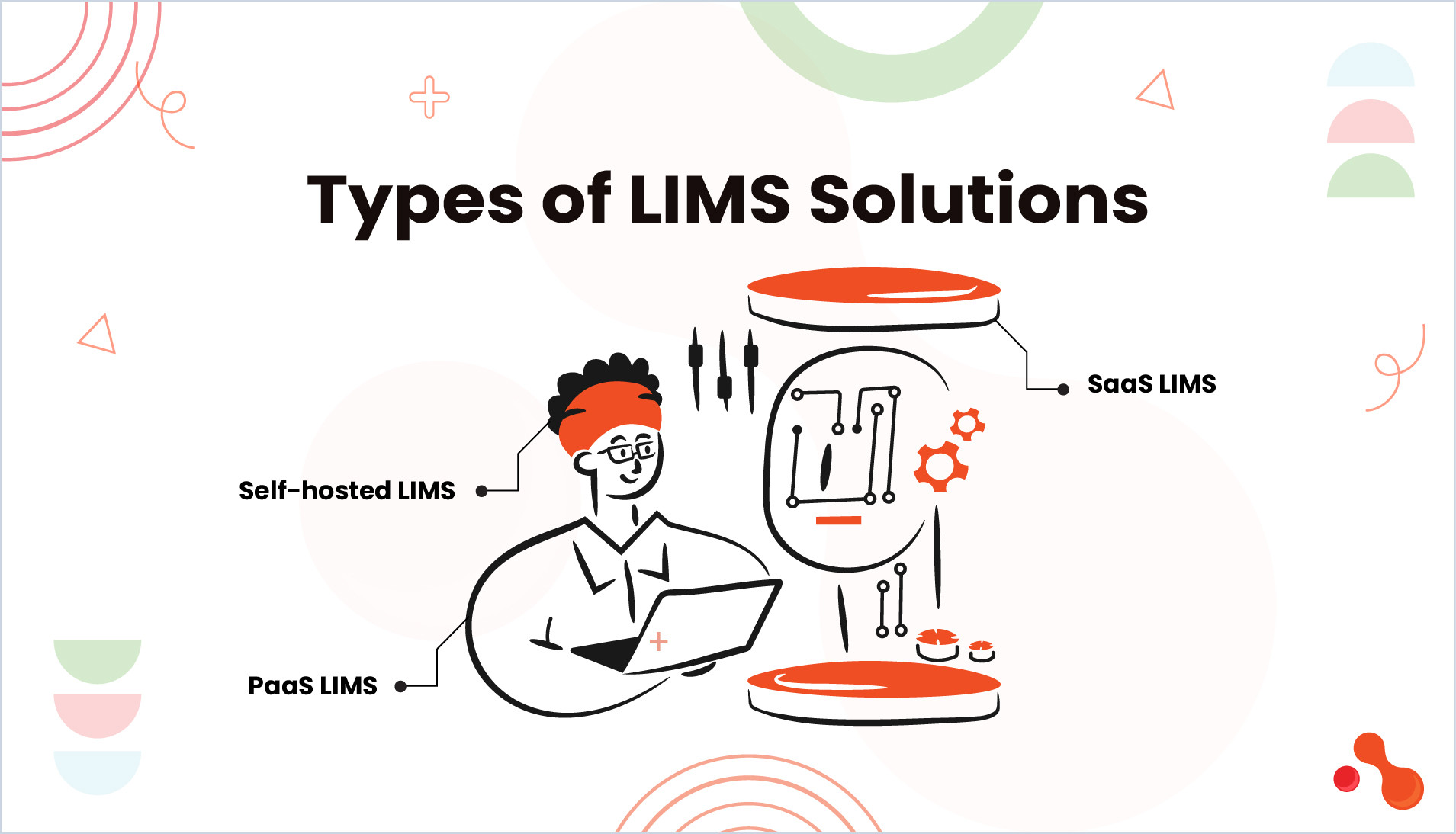
Laboratories have several options when choosing a LIMS, including self-hosted, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions. Each option presents different cost structures and levels of control over the system:
Self-hosted LIMS: Offers greater customization and control but requires significant investment in IT infrastructure and support.
PaaS LIMS: Provides a balance between customization and cost, reducing the need for extensive hardware investment.
SaaS LIMS typically have lower upfront costs and are managed entirely by the vendor, minimizing the need for internal IT resources.
Common Applications of a LIMS

The key reasons for implementing a LIMS often boil down to a combination of increasing efficiency, improving data accuracy, ensuring regulatory compliance, and facilitating better decision-making. Traditional methods of managing laboratory data, such as paper-based or basic spreadsheet systems are prone to human error, slow processes, and limited data analytics capabilities.
A LIMS modernizes these processes, centralizing data storage, automating repetitive tasks, and enabling data-driven decision-making. For laboratories aiming for growth, scalability, and precision, a LIMS is indispensable. In fact, the global LIMS market was valued at over $2.45 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to over $9.20 billion by 2036.
It is widely used in various types of laboratories for diverse applications, depending on the specific needs and industry. Here are some common applications of LIMS:
Sample Management
Tracking and Logging: Monitors the status and location of samples throughout their lifecycle, from reception to disposal.
Sample Labeling: Generates and manages barcodes and labels for accurate sample identification.
Chain of Custody: Maintains detailed records of sample handling and transfer to ensure traceability and accountability.
Data Management and Integration
Data Storage and Retrieval: Organizes and stores large volumes of experimental data for easy access.
Instrument Integration: Connects with lab instruments to automatically capture, analyze, and store data, minimizing manual entry errors.
Reporting and Visualization: Generates reports and visualizations to support data analysis, quality control, and decision-making.
Workflow Automation and Scheduling
Task Management: Automates routine laboratory tasks, test requests, and resource allocation.
Scheduling and Planning: Manages laboratory schedules for tests, resources, and equipment availability, optimizing workflow efficiency.
Compliance Workflows: Supports the creation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC)
Regulatory Compliance: Facilitates compliance with standards such as ISO 17025, GLP, GxP, and CLIA by maintaining accurate and complete records.
Audit Trails: Maintains audit trails to track changes in data, user actions, and system configurations for transparency.
Nonconformance Management: Identifies deviations and manages corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
Inventory and Reagent Management
Stock Management: Tracks inventory levels of reagents, chemicals, and consumables, alerting users when reordering is needed.
Batch Management: Manages the preparation and expiration tracking of reagents and batches to ensure that only approved materials are used.
Resource Allocation: Allocates equipment and resources efficiently, minimizing downtime and optimizing lab utilization.
Document Management
SOP Management: Centralizes storage of standard operating procedures (SOPs) and other critical documents.
Version Control: Manages document versions and updates to ensure that users always have access to the latest information.
Access Control: Provides role-based permissions to control document access and editing rights.
Regulatory and Compliance Reporting
Automated Compliance Reporting: Generates compliance reports for regulatory bodies like the FDA, EPA, or CLIA.
Data Integrity Assurance: Ensures the integrity and traceability of data, supporting audits and regulatory inspections.
Validation and Certification: Helps in the validation and certification of laboratory processes, ensuring they meet industry standards.
Clinical and Research Applications
Patient Data Management: For clinical labs, it can manage patient data, test requests, and results.
Research Data Management: In research settings, it aids in managing experimental protocols, hypotheses, and outcomes.
Biobank Management: Manages biobanks and sample storage facilities, ensuring long-term data integrity and sample traceability.
Environmental and Chemical Analysis
Compliance Testing: Manages environmental sample data for compliance testing and reporting.
Chemical Inventory Management: Tracks the use of chemicals and hazardous materials to support regulatory compliance.
Analytical Testing: Facilitates complex chemical analyses, providing comprehensive data tracking and reporting tools.
Pharmaceutical and Biotech Laboratories
Drug Development Workflow: Supports drug development processes, from preclinical studies to clinical trials.
Batch Release and Stability Testing: Manages data for batch release, stability testing, and manufacturing quality control.
GxP Compliance: Ensures compliance with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP), Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and Good Clinical Practices (GCP).
Forensics and Legal Testing
Chain of Custody Management: Maintains detailed chain-of-custody records to ensure the legal integrity of forensic samples.
Evidence Management: Manages forensic samples, evidence handling, and analytical testing data for legal proceedings.
Court-Ready Reporting: Prepares standardized reports suitable for submission in legal cases.
Overall, a LIMS is an essential tool for improving laboratory productivity, data accuracy, and compliance across various industries, including healthcare, pharmaceuticals, environmental sciences, and more. The LIMS market is expected to grow at a rate of 11.80% from 2024 to 2036 globally.
Unlock the potential of LIMS for your business!
Take advantage of its numerous applications like streamlined workflows, data accuracy, and compliance management. Ready to transform your lab operations? Start developing a customized LIMS with Acquaint Softtech today!
Cost Factors Involved in Implementing a LIMS
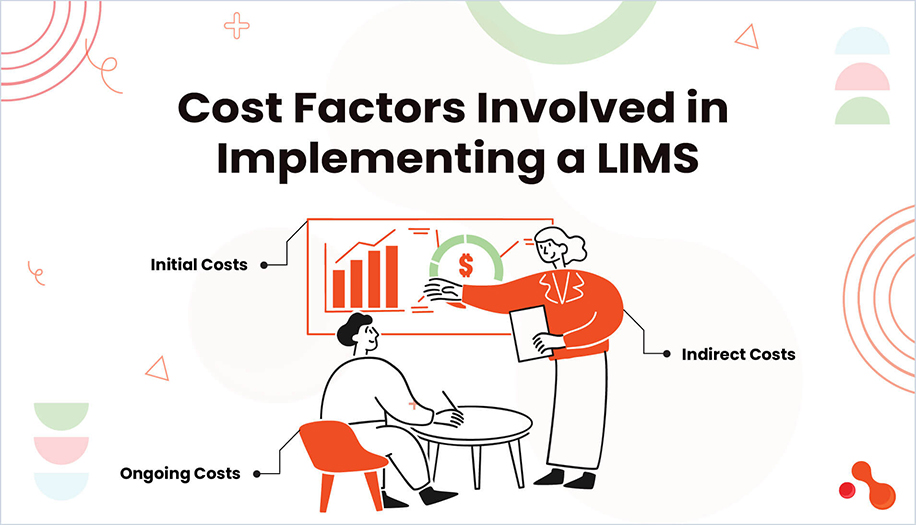
Implementing a LIMS is an investment that involves both upfront and ongoing costs. These costs can vary based on the size of the lab, the type of LIMS (cloud-based or on-premises), and the specific needs of the lab. Here's a breakdown of the main cost components:
Initial Costs
Software Licensing and Setup Fees: The cost of this type of laboratory software depends on several factors, including the vendor, the number of users, and whether the solution is cloud-based or on-premises. Cloud-based systems often have lower upfront costs but may incur ongoing subscription fees. On-premises solutions may have a significant upfront cost for software licenses, server hardware, and setup fees.
Hardware and Infrastructure Costs: For on-premises LIMS, you will need hardware to run the system, including servers, networking equipment, and possibly new computers for lab staff. Cloud-based LIMS may not require significant hardware investments, but you will need reliable internet connectivity and possibly upgrades to your existing IT infrastructure.
Customization Costs: Most laboratories have unique workflows and specific data management needs, which means the out-of-the-box LIMS solution may not meet all of your requirements. Customization of workflows, reports, and integrations with laboratory instruments can add to the initial cost. Complex customizations can drive up costs significantly, depending on the extent of changes required.
Training Costs: Training is essential to ensure that laboratory staff can effectively use the new LIMS. Training programs, workshops, and online tutorials can add to the overall cost of implementation. Moreover, it may take some time for staff to become proficient in using the system, which can temporarily reduce productivity.
Data Migration: If your laboratory has years of legacy data stored in spreadsheets or other systems, migrating this data to the LIMS can be both time-consuming and expensive. Data migration costs will depend on the volume of data, the complexity of the migration process, and any necessary data cleaning before migration.
Ongoing Costs
Maintenance and Support: LIMS software typically requires ongoing support and maintenance to ensure that it functions optimally and remains secure. These costs may include software updates, bug fixes, and technical support. Depending on the vendor, maintenance fees may be included in the subscription cost or charged separately.
Subscription Fees: For cloud-based LIMS, there are typically ongoing subscription fees based on the number of users or the amount of data stored. These fees are paid monthly or annually, and while they may be lower than the upfront cost of an on-premises system, they represent a continual cost for the lab.
Security and Compliance: Ensuring that the LIMS complies with regulatory standards (such as HIPAA, GLP, or ISO) and protecting sensitive data is crucial. This may involve ongoing security measures such as encryption, regular audits, and cybersecurity training for staff. These additional layers of protection can come with extra costs.
Indirect Costs
Disruption During Implementation: The transition period can disrupt normal laboratory operations, leading to temporary losses in productivity and efficiency.
Change Management: Staff may resist adopting a new system, which can require additional time and resources for change management.
Benefits of Implementing a LIMS

While there are substantial costs involved in implementing a LIMS, the long-term benefits can significantly outweigh the initial investment. Let’s explore the key advantages of implementing a LIMS:
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: One of the most significant benefits of LIMS is the automation of routine tasks such as sample tracking, data entry, and report generation. By automating these processes, laboratory staff can focus on more complex and value-added activities, increasing overall productivity.
Faster Data Access and Retrieval: A LIMS centralizes data storage, making it easier for lab personnel to access and retrieve information. This eliminates the need for manual searches through paper records or spreadsheets, saving time and improving the speed of decision-making.
Improved Workflow Management: LIMS systems streamline workflows by automatically assigning tasks, notifying staff when actions are required, and tracking the status of ongoing experiments. This ensures that processes run smoothly and efficiently, reducing bottlenecks.
Reduction of Human Errors: Manual data entry is prone to errors, which can compromise the integrity of lab results and lead to costly mistakes. A LIMS minimizes human error by automating data capture, ensuring that information is recorded accurately and consistently.
Data Validation and Integrity: LIMS systems include validation features that ensure data entered into the system meets predefined standards. This ensures data accuracy and integrity, which is crucial for laboratories operating under regulatory requirements such as Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) or ISO certifications.
Version Control and Audit Trails: A LIMS provides audit trails that track changes to data, ensuring full traceability and accountability. This is particularly important in regulated industries where compliance with legal and quality standards is required.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards: Many laboratories operate in industries with strict regulatory standards. A LIMS helps ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 17025, HIPAA, and FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 by providing built-in features such as audit trails, electronic signatures, and data encryption.
Streamlined Quality Control Processes: LIMS systems offer features specifically designed for quality control, such as sample validation, instrument calibration reminders, and automated reporting. This helps maintain the highest quality standards in laboratory operations.
Better Data Management and Security: Centralized Data Storage: A LIMS provides a centralized database for storing all laboratory data, ensuring that information is easily accessible and secure. This eliminates the risk of data loss or mismanagement often associated with decentralized storage methods such as paper records or spreadsheets.
Data Security and Access Control: LIMS systems offer enhanced security features such as role-based access control, encryption, and two-factor authentication. These measures ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of breaches or unauthorized access.
Scalability and Adaptability: As laboratories grow and take on more samples, the complexity of managing data increases. A LIMS can quickly scale to handle larger volumes of data, ensuring that workflows remain efficient even as demand grows.
Adaptation to New Workflows: LIMS systems are highly adaptable and can be customized to meet the unique needs of a laboratory. This ensures that the system can evolve alongside changes in lab operations, new methodologies, or industry regulations.
Reduction in Operational Costs: A LIMS can lead to substantial cost savings over time by automating processes, reducing errors, and improving efficiency. Laboratories can save money on labor costs, reduce the need for rework, and avoid penalties associated with non-compliance.
Better Resource Utilization: LIMS systems provide insights into lab operations, helping managers allocate resources more efficiently. This includes optimizing equipment usage, scheduling staff more effectively, and ensuring that consumables are used optimally.
Improved Reporting and Decision-Making: Automated Reporting: A LIMS can generate reports automatically, providing laboratory managers with real-time insights into lab performance, sample status, and quality metrics. This data is crucial for making informed decisions and identifying areas for improvement.
Data-Driven Insights: With all data stored centrally and accessible at any time, a LIMS allows labs to leverage data analytics tools to gain insights into trends, performance, and bottlenecks. These insights drive better decision-making and continuous improvement efforts.
Benefit from a cost-effective LIMS solution today!
Streamline lab processes, reduce overhead costs, and enhance productivity without breaking the bank. Get started with Acquaint Softtech now! And witness the impact on your operations!
Transparency In Developing LIMS Solution
When evaluating the cost of a LIMS, it's essential to consider the several hidden costs. Hiring processionals from a well-established software development outsourcing company like Acquaint Softtech, will ensure complete transparency.
A fitting quote: “If you deprive yourself of outsourcing and your competitors do not, you’re putting yourself out of business.” – Lee Kuan Yew, Former Prime Minister of Singapore
This includes full disclosure of the hidden costs like:
Pricing Structure: LIMS software can be priced in various ways, such as per user, per concurrent user, or module. Additionally, tiered packages may have different pricing, volume discounts, or hidden costs not immediately obvious in an initial quote.
Data Migration and Integration: The cost of migrating existing data to the new LIMS and integrating it with other laboratory equipment or software can be significant.
IT Infrastructure Support: The cost of maintaining the hardware and software required to support the LIMS, including hardware maintenance expenses, security measures, and data protection costs, can add up quickly.
Daily Operational Support: The cost of ongoing technical assistance, user license fees, and periodic upgrades can also impact the overall cost of the LIMS.
Hire remote developers from Acquaint Softtech to take advantage of our extensive experience and highly skilled developers. We have expertise in a wide range of technologies, besides which we are also one of the few firms in Asia that is an official Laravel partner.
The Verdict
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) for implementing a LIMS should weigh all associated costs against the expected benefits:
Identify and Quantify Costs: List all initial, ongoing, and hidden costs associated with implementing and maintaining the LIMS. This includes:
Software licensing and customization
Training and onboarding
Infrastructure upgrades
Maintenance and support fees
Downtime costs
Identify and Quantify Benefits: Estimate the financial value of the tangible benefits, such as:
Labor cost savings
Reduced error rates and rework
Increased sample throughput
Reduced compliance costs
Assign dollar values where possible and identify areas of improvement where benefits can be quantified.
Compare Costs and Benefits: Once you've quantified both costs and benefits, calculate the net benefit of the LIMS by subtracting the total costs from the total benefits. This will provide you with a clearer picture of the system's ROI.
Consider Intangible Benefits: While intangible benefits are more challenging to quantify, they should still be factored into the decision-making process. These benefits, such as improved laboratory reputation and employee satisfaction, can have a significant impact on the long-term success of the laboratory.
Tangible Benefits: These benefits can be quantified and are essential for calculating return on investment (ROI).
Reduction in manual labor hours
Decrease in sample handling errors
Faster turnaround times for sample analysis
Lower operational costs
Intangible Benefits: While harder to measure, intangible benefits are equally important. These include:
Improved laboratory reputation due to enhanced accuracy and compliance
Higher employee satisfaction from using an efficient system
Better customer satisfaction from faster reporting and reliable data
Stronger regulatory relationships and fewer compliance issues
These benefits contribute to long-term growth and sustainability for laboratories.
Conclusion
Implementing a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a substantial investment for any laboratory, but the long-term benefits can far outweigh the costs. By improving efficiency, reducing errors, enhancing regulatory compliance, and providing better data management, a LIMS offers laboratories the tools they need to grow and thrive in today’s competitive environment.
Through a thorough cost-benefit analysis, laboratories can assess whether a LIMS is the right choice for their unique needs and ensure that they maximize the return on their investment.
Outsource the development of your LIMS solution today!
Focus on what you do best while our experts handle the technical details. Achieve a tailored, efficient system that meets your specific needs. Contact Acquaint Softtech to get started!
Table of Contents
Get Started with Acquaint Softtech
- 13+ Years Delivering Software Excellence
- 1300+ Projects Delivered With Precision
- Official Laravel & Laravel News Partner
- Official Statamic Partner